People with heart disease may receive different care because of how race is interpreted in health risk calculators and other tools that help clinicians make treatment decisions.
Apr 29 2024American Heart Association The American Heart Association, a global force for healthier lives for all celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service, awarded four new grants this month to support scientific research that will evaluate the use of race in predicting heart disease risk and in turn help develop tools that are free of bias.
The newly funded principal investigators join six previous awardees who are part of a two-year scientific research strategy funded by a grant from the Doris Duke Foundation to study the complex issue of how race and ethnicity factor into clinical care algorithms and risk prediction tools. The grants are $50,000 each.
Clinical algorithms are formulas used to analyze health data and help determine a person's risk for disease or guide their treatment decisions. Age, weight, information from blood or imaging tests, personal health history and health habits -; like physical activity and smoking -; are among the many types of data used by clinical algorithms.
These innovative research projects are focused on testing many different risk models that include a variety of health variables in an effort to remove racial bias from clinical algorithms. Our hope is that this research helps change the discourse about how race is considered in risk calculation.
Heart Disease Research Atherosclerosis Calcium Cardiovascular Disease Computed Tomography Coronary Heart Disease CT Health Disparities Imaging Ph Stroke Tomography
Ireland Latest News, Ireland Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 'Miracle' weight-loss drugs could have reduced health disparities: Instead they got worseThe American Heart Association calls them 'game changers.'
'Miracle' weight-loss drugs could have reduced health disparities: Instead they got worseThe American Heart Association calls them 'game changers.'
Read more »
 Study shows link between association between air pollution, stress, and heart health riskA study in more than 3,000 US counties, with 315 million residents, has suggested that air pollution is linked with stress and depression, putting under-65-year-olds at increased risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
Study shows link between association between air pollution, stress, and heart health riskA study in more than 3,000 US counties, with 315 million residents, has suggested that air pollution is linked with stress and depression, putting under-65-year-olds at increased risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
Read more »
 William's heart-to-heart with father that shaped his future with Kate MiddletonPrince William has always been close to his father, King Charles, and has often turned to him for advice and guidance - including when it came to his future with Kate Middleton
William's heart-to-heart with father that shaped his future with Kate MiddletonPrince William has always been close to his father, King Charles, and has often turned to him for advice and guidance - including when it came to his future with Kate Middleton
Read more »
 Study Finds Empagliflozin Does Not Significantly Reduce Heart Failure Hospitalizations or Death After Heart AttackThe use of the SGLT-2 inhibitor empagliflozin after a heart attack did not show a significant benefit in reducing overall heart failure hospitalizations or death from any cause, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology's Annual Scientific Session. However, researchers said the drug may be helpful in reducing heart failure risks, including hospitalization, following a heart attack.
Study Finds Empagliflozin Does Not Significantly Reduce Heart Failure Hospitalizations or Death After Heart AttackThe use of the SGLT-2 inhibitor empagliflozin after a heart attack did not show a significant benefit in reducing overall heart failure hospitalizations or death from any cause, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology's Annual Scientific Session. However, researchers said the drug may be helpful in reducing heart failure risks, including hospitalization, following a heart attack.
Read more »
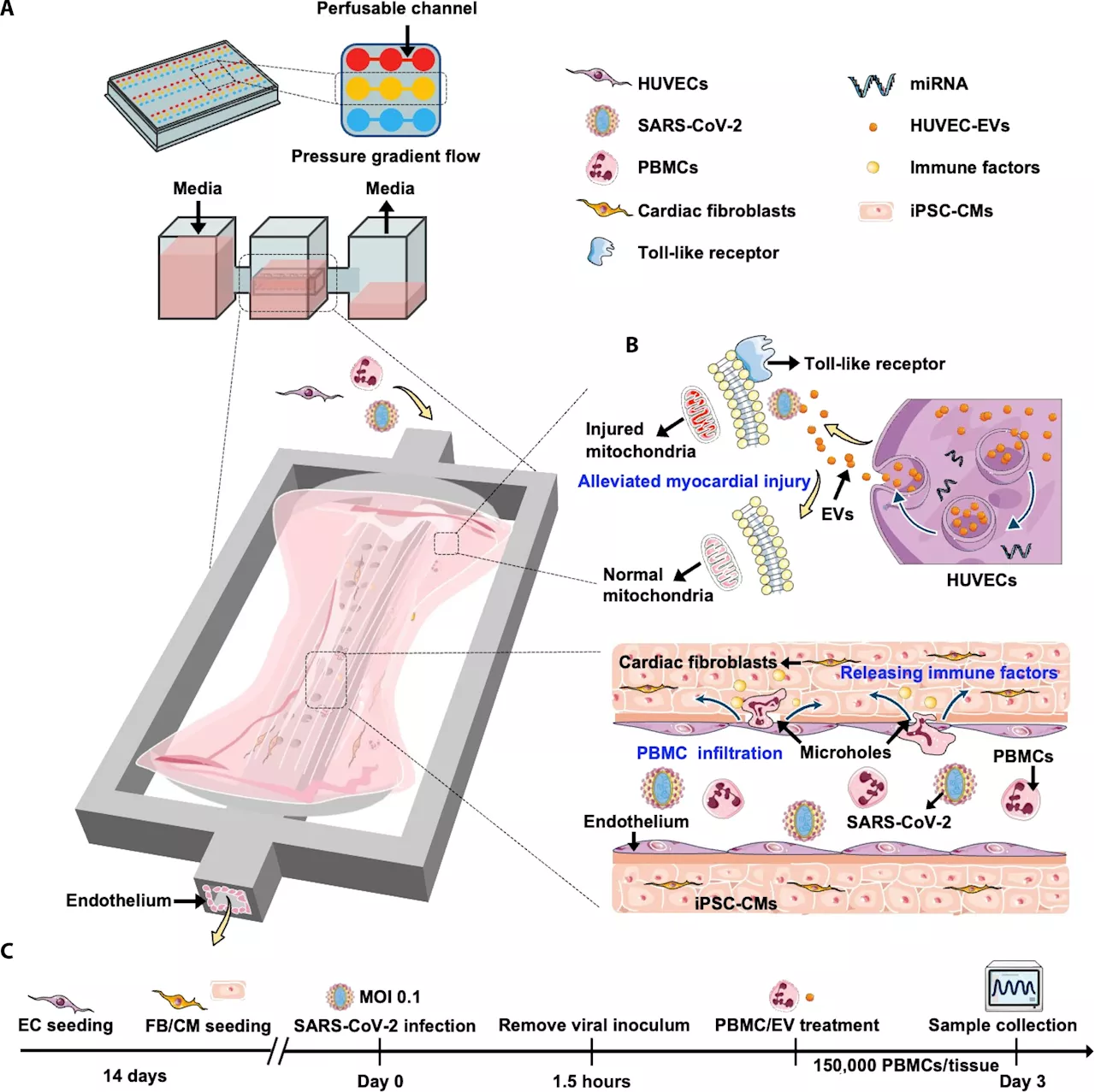 Heart-on-a-chip model used to glean insights into COVID-19-induced heart inflammationResearchers at the University of Toronto and its partner hospitals have created a unique heart-on-a-chip model that is helping untangle the causes of COVID-19-induced heart inflammation and uncover strategies to reduce its impact.
Heart-on-a-chip model used to glean insights into COVID-19-induced heart inflammationResearchers at the University of Toronto and its partner hospitals have created a unique heart-on-a-chip model that is helping untangle the causes of COVID-19-induced heart inflammation and uncover strategies to reduce its impact.
Read more »
 Heart pump improves survival after severe heart attacksImplantation of the Impella CP micro-axial flow pump in the hours after a heart attack significantly increased the rate of survival at six months among people suffering cardiogenic shock, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology's Annual Scientific Session.
Heart pump improves survival after severe heart attacksImplantation of the Impella CP micro-axial flow pump in the hours after a heart attack significantly increased the rate of survival at six months among people suffering cardiogenic shock, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology's Annual Scientific Session.
Read more »
