From connectomics to behavioural biology, artificial intelligence is making it faster and easier to extract information from images.
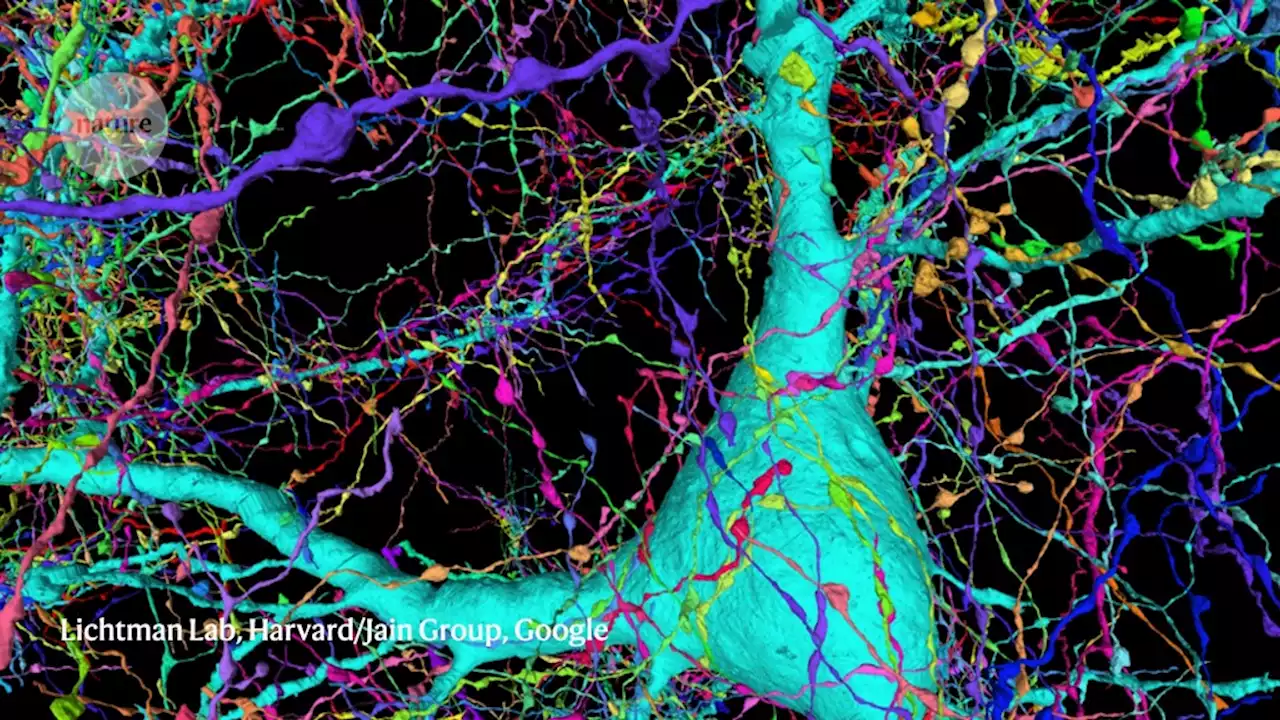
One cubic millimetre doesn’t sound like much. But in the human brain, that volume of tissue contains some 50,000 neural ‘wires’ connected by 134 million synapses. Jeff Lichtman wanted to trace them all.
Deep learning is an artificial-intelligence technique that relies on many-layered artificial neural networks inspired by how neurons interconnect in the brain. Based as they are on black-box neural networks, the algorithms have their limitations. Those include a dependence on massive data sets to teach the network how to identify features of interest, and a sometimes inscrutable way of generating results.
Alternatively, researchers can install and run dedicated software. For instance, ilastik has a point-and-click interface to help detect not just cells and nuclei but also features such as microtubules and vesicles. Co-developer Anna Kreshuk, a computer scientist at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in Heidelberg, Germany, and her colleagues are now working to improve the software’s ability to train neural networks for tasks such as classification and segmentation.
Deep-learning algorithms effectively operate as black boxes, but some tools can provide clues to their reasoning. “You can tell, for example, which part of an image was most important in making a particular decision,” says Cimini. “The image analysis tasks in connectomics are very difficult,” Jain says. “You have to be able to trace these thin wires, the axons and dendrites of a cell, across large distances, and conventional image-processing methods made so many mistakes that they were basically useless for this task.” These wires can be thinner than a micrometre and extend over hundreds of micrometres or even millimetres of tissue.