How lipid metabolites in the gut aid in regulatory T-cell differentiation Cell Metabolites Microbiome TCell Gut microbiota SciReports
By Dr. Priyom Bose, Ph.D.Jun 6 2023Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. Previous research has documented the impact of gut microbiota-derived hydrophilic metabolites on immune cell functions and development. However, the immunomodulatory effects of gut microbiota-derived lipids are not fully understand.
Background Treg cells are important in inducing mucosal tolerance, as they mute the immune response to benign foreign antigens and, as a master transcription factor, express forkhead box P3 . Furthermore, Treg cells inhibit the activation of effector T-cells and express cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 .
Commensal bacteria lead to Treg cell development through different mechanisms, including the use of polyunsaturated fatty acid as a substrate to produce lipophilic metabolites. Previous studies have shown that the metabolism of fatty acids by commensal bacteria regulates host immunity; however, the effects of lipophilic metabolites derived from the gut microbiota on other immune cell populations remain unknown.
Related StoriesA Treg-inducing activity in the methyl formate fraction of the fecal lipid extract was detected. Moreover, 9,10-DiHOME and atRA were identified as the bioactive constituents with Treg-inducing activity using target lipidomics analysis. The activation of PPARγ in DCs was seen to upregulate Aldh1a2, thereby promoting Treg differentiation. More research is needed to determine the mechanism through which 9,10-DiHOME confers Treg-inducing activity on DCs.
The concentration of 9,10-DiHOME in the colonic tissue and feces was reduced during the progression of colitis. Thus, the fecal concentration of 9,10-DiHOME could serve as an early biomarker of colitis.
Ireland Latest News, Ireland Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Multiple sclerosis: Immune cell invasion enabled by blood-brain barrier breakdownBlood-brain barrier breakdown in multiple sclerosis leads to immune cell infiltration into the central nervous system. Antigen presentation at the barrier promotes CD8+ T cell entry, triggering focal breakdown and hindering their invasion.
Multiple sclerosis: Immune cell invasion enabled by blood-brain barrier breakdownBlood-brain barrier breakdown in multiple sclerosis leads to immune cell infiltration into the central nervous system. Antigen presentation at the barrier promotes CD8+ T cell entry, triggering focal breakdown and hindering their invasion.
Read more »
 Prison boss says 'no plans' to increase cell searches amid rise in drug findsFiona Cruickshanks claims guards spending more time searching for contraband would mean less “meaningful engagement” with prisoners.
Prison boss says 'no plans' to increase cell searches amid rise in drug findsFiona Cruickshanks claims guards spending more time searching for contraband would mean less “meaningful engagement” with prisoners.
Read more »
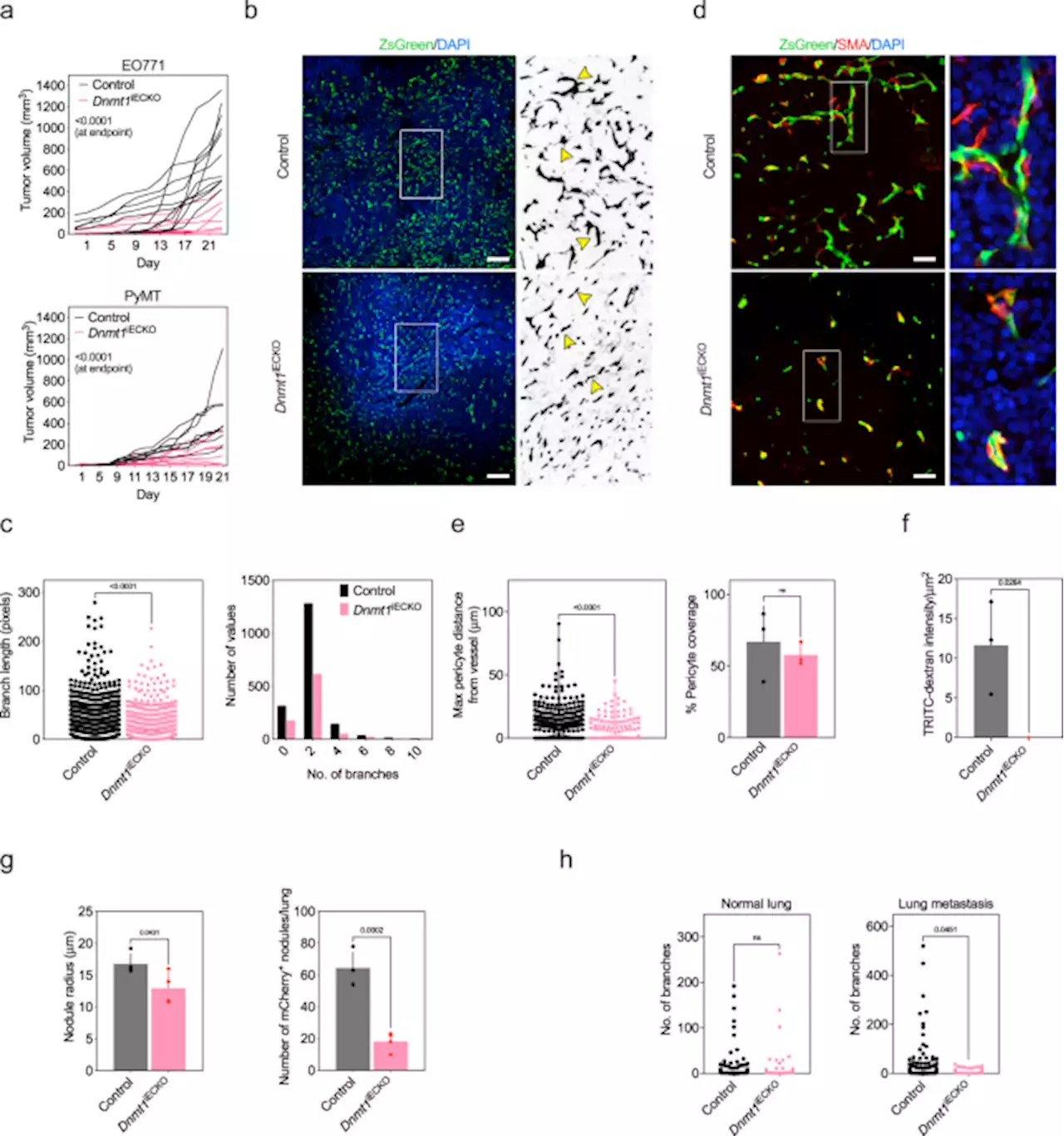 Priming a vascular-selective cytokine response permits CD8+ T-cell entry into tumors - Nature CommunicationsIt has been reported that inhibition of the epigenetic regulator DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) is associated with improved response to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB). Here the authors show that conditional deletion of Dnmt1 in endothelial cells is sufficient to promote T cell infiltration, reduce tumor growth and enhance ICB response in preclinical models.
Priming a vascular-selective cytokine response permits CD8+ T-cell entry into tumors - Nature CommunicationsIt has been reported that inhibition of the epigenetic regulator DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) is associated with improved response to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB). Here the authors show that conditional deletion of Dnmt1 in endothelial cells is sufficient to promote T cell infiltration, reduce tumor growth and enhance ICB response in preclinical models.
Read more »
 Cyclists wearing helmets seen as 'less human' than those without, researchers find'Our findings add to this growing research, suggesting that cyclists wearing safety attire, particularly high-visibility vests, may be dehumanised more so than cyclists without safety attire'
Cyclists wearing helmets seen as 'less human' than those without, researchers find'Our findings add to this growing research, suggesting that cyclists wearing safety attire, particularly high-visibility vests, may be dehumanised more so than cyclists without safety attire'
Read more »
 Older children under-five living in low incomes large families in rural areas are most vulnerable to malaria infectionOlder children under-five living in low incomes large families in rural areas are most vulnerable to malaria infection PLOSONE rural LMICs LMIC vulnerable malaria infection
Older children under-five living in low incomes large families in rural areas are most vulnerable to malaria infectionOlder children under-five living in low incomes large families in rural areas are most vulnerable to malaria infection PLOSONE rural LMICs LMIC vulnerable malaria infection
Read more »
 Quantifying the impact of intermittent fasting on appetiteQuantifying the impact of intermittent fasting on appetite Nutrients_MDPI BristolUni intermittentfasting fasting IF diet appetite nutrients
Quantifying the impact of intermittent fasting on appetiteQuantifying the impact of intermittent fasting on appetite Nutrients_MDPI BristolUni intermittentfasting fasting IF diet appetite nutrients
Read more »
