Can plant-derived nutrients alter gut bacteria to affect brain function? Scientists investigated this question in a study of overweight adults. Their findings suggest that dietary fiber can exert influence on both the composition of gut bacteria and the reward signals in the brain and associated food decision-making.
Prebiotics are used to foster the colonisation of beneficial bacteria in the gut. These indigestible dietary fibres are found in plant-derived foods such as onions, leeks, artichokes, wheat, bananas, and in high concentrations in chicory root. They support gut health by promoting the growth and activity of beneficial gut bacteria. Researchers have now investigated whether certain prebiotics can also influence brain function by improving communication between the gut microbiome and the brain.
Young to middle-aged adults with overweight were selected for the study who followed an omnivorous, Western diet. The 59 volunteers consumed 30 grams of inulin, a prebiotic from chicory root, daily for 14 days. During functional MRI imaging, participants were shown pictures of food and asked how much they desired to eat the meals depicted. Following the MRI experiment, they were provided with their highest rated dish and asked to consume it.
The findings, derived from advanced neuroimaging, next-generation sequencing of gut bacteria, and combined analyses of potential metabolic pathways, suggest that functional microbial changes may underlie the altered brain response towards high-caloric food cues. Fasting blood samples from the participants underwent analysis for gastrointestinal hormones, glucose, lipids, and inflammatory markers.
Researchers found that higher levels of dietary fiber are associated with a reduced risk of developing dementia. In a large-scale study, over 3500 Japanese adults completed a dietary survey and were ...
Ireland Latest News, Ireland Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Scientists Discover Simple New Remedy for Garlic BreathScience, Space and Technology News 2023
Scientists Discover Simple New Remedy for Garlic BreathScience, Space and Technology News 2023
Read more »
 Scientists Discover Hidden Threat to the Great Barrier ReefScience, Space and Technology News 2023
Scientists Discover Hidden Threat to the Great Barrier ReefScience, Space and Technology News 2023
Read more »
 Beyond Umami: Scientists Discover a Sixth Basic TasteScience, Space and Technology News 2023
Beyond Umami: Scientists Discover a Sixth Basic TasteScience, Space and Technology News 2023
Read more »
 Scientists upcycle polyesters through new waste-free, scalable processResearchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new chemical process which upcycles polyesters, including PET in plastic bottles, to morpholine amide, a versatile and valuable building block for synthesizing a vast range of compounds. The reaction is high yield, waste-free, does not require harmful chemicals, and is easily scalable. The team have successfully broken the, often costly, closed-loop recycling loop of plastic waste, allowing upcycling to more valuable products.
Scientists upcycle polyesters through new waste-free, scalable processResearchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new chemical process which upcycles polyesters, including PET in plastic bottles, to morpholine amide, a versatile and valuable building block for synthesizing a vast range of compounds. The reaction is high yield, waste-free, does not require harmful chemicals, and is easily scalable. The team have successfully broken the, often costly, closed-loop recycling loop of plastic waste, allowing upcycling to more valuable products.
Read more »
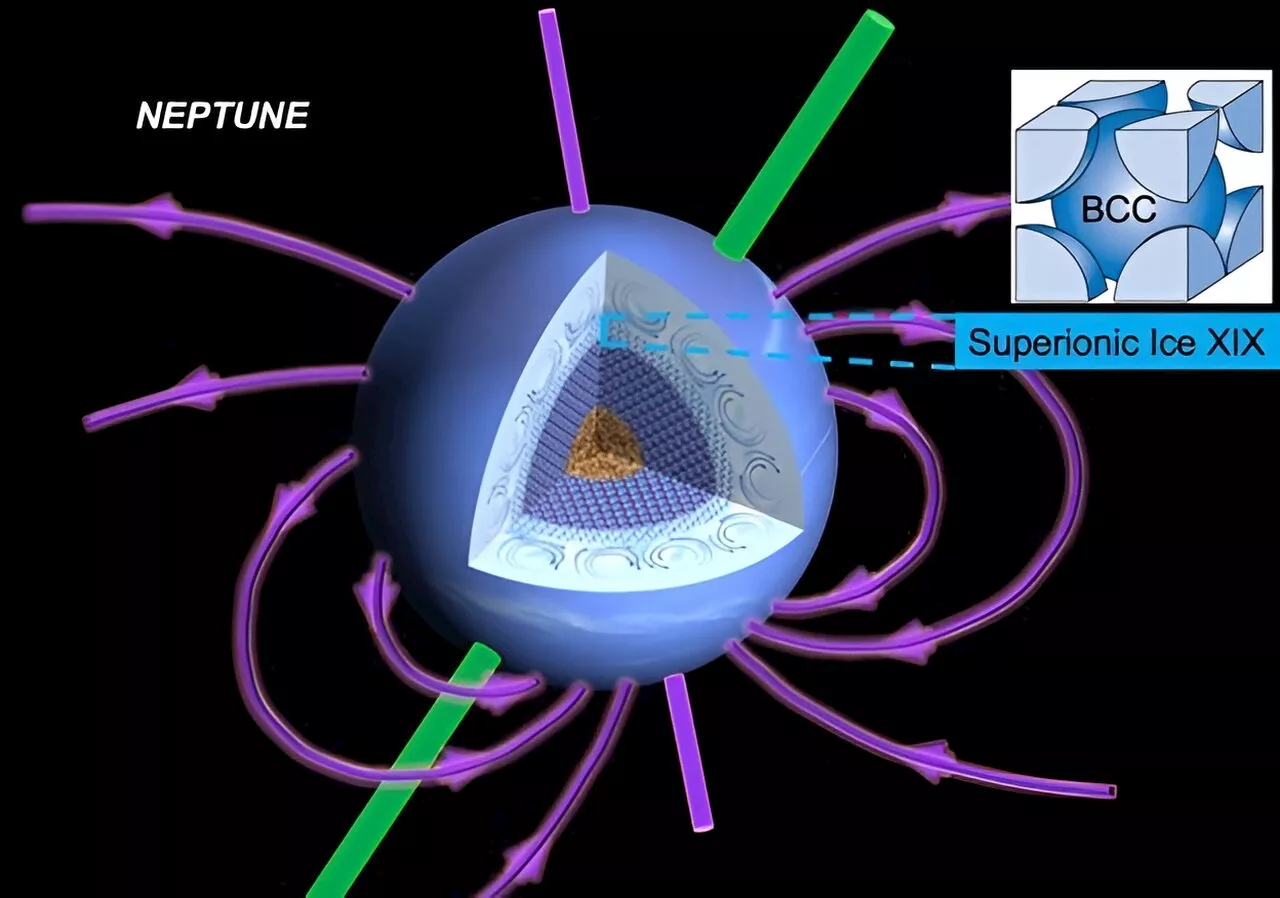 Scientists discover a new phase of high-density, ultra-hot iceThe outer planets of our solar system, Uranus and Neptune, are water-rich gas giants. These planets have extreme pressures 2 million times the Earth's atmosphere. They also have interiors as hot as the surface of the sun. Under these conditions, water exhibits exotic, high-density ice phases.
Scientists discover a new phase of high-density, ultra-hot iceThe outer planets of our solar system, Uranus and Neptune, are water-rich gas giants. These planets have extreme pressures 2 million times the Earth's atmosphere. They also have interiors as hot as the surface of the sun. Under these conditions, water exhibits exotic, high-density ice phases.
Read more »
 Scientists Announce That Unexplored Parts Of Ocean Probably Contain More WaterCAMBRIDGE, MA—Advancing a bold new theory that could revolutionize the way scientists think about the planet, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology announced Monday that the unexplored parts of the world’s oceans probably contain more water. “While we can’t say with certainty what lay in those deep…
Scientists Announce That Unexplored Parts Of Ocean Probably Contain More WaterCAMBRIDGE, MA—Advancing a bold new theory that could revolutionize the way scientists think about the planet, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology announced Monday that the unexplored parts of the world’s oceans probably contain more water. “While we can’t say with certainty what lay in those deep…
Read more »
