Research published in Nature reports a deep reinforcement learning architecture to design controllers for the magnetic confinement of plasmas in tokamaks
. The interaction trajectories are sampled at random from the buffer by a ‘learner’, which executes the MPO algorithm to update the control-policy parameters. During training, the executed control policy is stochastic to explore successful control options. This stochastic policy is represented by a diagonal Gaussian distribution over coil actions.
Each episode corresponds to a single simulation run that terminates either when a termination condition is hit, which we will discuss below, or when a fixed simulation time has passed in the episode. This fixed time was 0.2 s for the droplets, 0.5 s in the case of Extended Data Fig., and 1 s otherwise. Each episode is initialized from an equilibrium state at the preprogrammed handover time, which was reconstructed from a previous experiment on TCV.
Our training loop emulates the control frequency of 10 kHz. At each step, the policy is evaluated using the observation from the previous step. The resulting action is then applied to the simulator, which is then stepped. Observations and rewards are also collected at the 10-kHz control frequency, resulting in training data collected at 0.1 ms intervals. For our simulation, we chose a time step of 50 kHz. Hence, for each evaluation of the policy, five simulation time steps are computed.
As RL only interacts sample-wise with the environment, the policy could be fine-tuned further with data from interacting with the plant. Alternatively, one might imagine leveraging the database of past experiments performed on TCV to improve the policy. However, it is unclear if the data are sufficiently diverse, given the versatility of TCV and the fact that the same plasma configuration can be achieved by various coil-voltage configurations.
The process for combining these multiple objectives into a single scalar is as follows. First, for each objective, the difference between the actual and target values is computed, and then transformed with a non-linear function to a quality measure between 0 and 1. In the case of a vector-valued objective , the individual differences are first merged into a single scalar through a ‘combiner’, a weighted non-linear function.
Ireland Latest News, Ireland Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
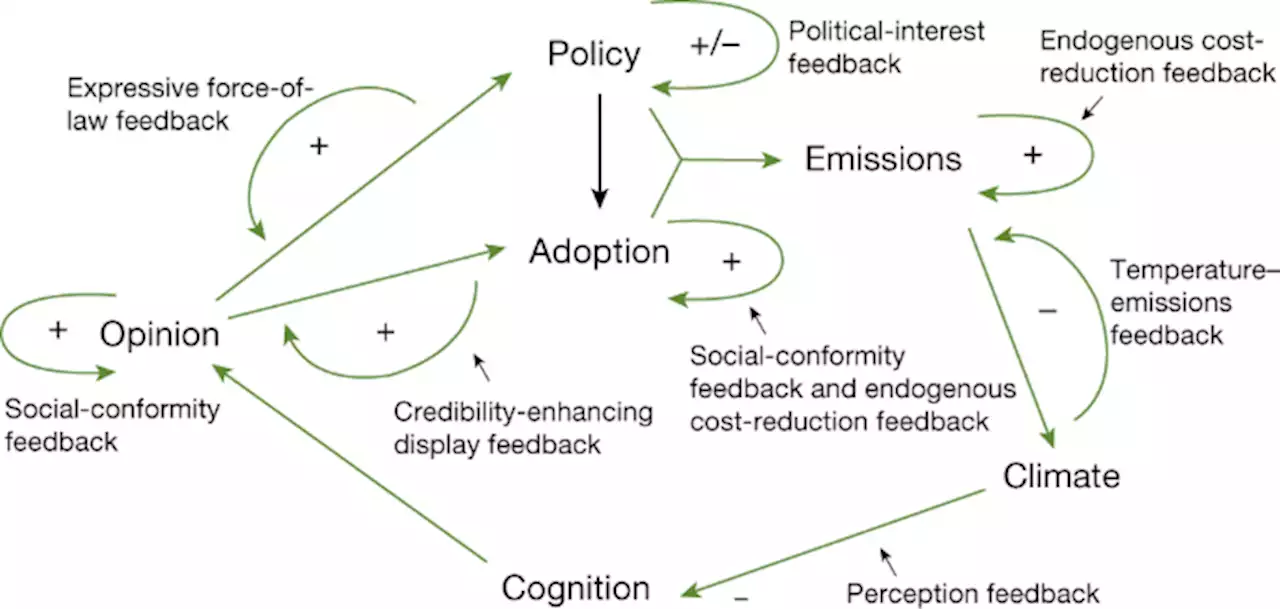 Determinants of emissions pathways in the coupled climate–social system - NatureA new modelling study uncovers how perceptions of climate change, the cost and effectiveness of mitigation strategies, and political responses all interact to determine the course of global warming over the 21st century
Determinants of emissions pathways in the coupled climate–social system - NatureA new modelling study uncovers how perceptions of climate change, the cost and effectiveness of mitigation strategies, and political responses all interact to determine the course of global warming over the 21st century
Read more »
 Differential clock comparisons with a multiplexed optical lattice clock - NatureMultiple ultracold ensembles of strontium atoms are trapped in the same optical lattice, realizing a multiplexed optical clock where precision measurements can benefit from having all atoms share the same trapping light and clock laser.
Differential clock comparisons with a multiplexed optical lattice clock - NatureMultiple ultracold ensembles of strontium atoms are trapped in the same optical lattice, realizing a multiplexed optical clock where precision measurements can benefit from having all atoms share the same trapping light and clock laser.
Read more »
 Differential mechanisms underlie trace and delay conditioning in Drosophila - NatureTrace and delay conditioning experiments in Drosophila reveal the different neurons and signalling mechanisms that underlie this behaviour and highlight similarities with observations of learning experiences in mammals.
Differential mechanisms underlie trace and delay conditioning in Drosophila - NatureTrace and delay conditioning experiments in Drosophila reveal the different neurons and signalling mechanisms that underlie this behaviour and highlight similarities with observations of learning experiences in mammals.
Read more »
 Silence by name, silence by nature: the firm reinventing the scooter | AutocarSilence by name, silence by nature: the firm reinventing the scooter via M0veElectric
Silence by name, silence by nature: the firm reinventing the scooter | AutocarSilence by name, silence by nature: the firm reinventing the scooter via M0veElectric
Read more »
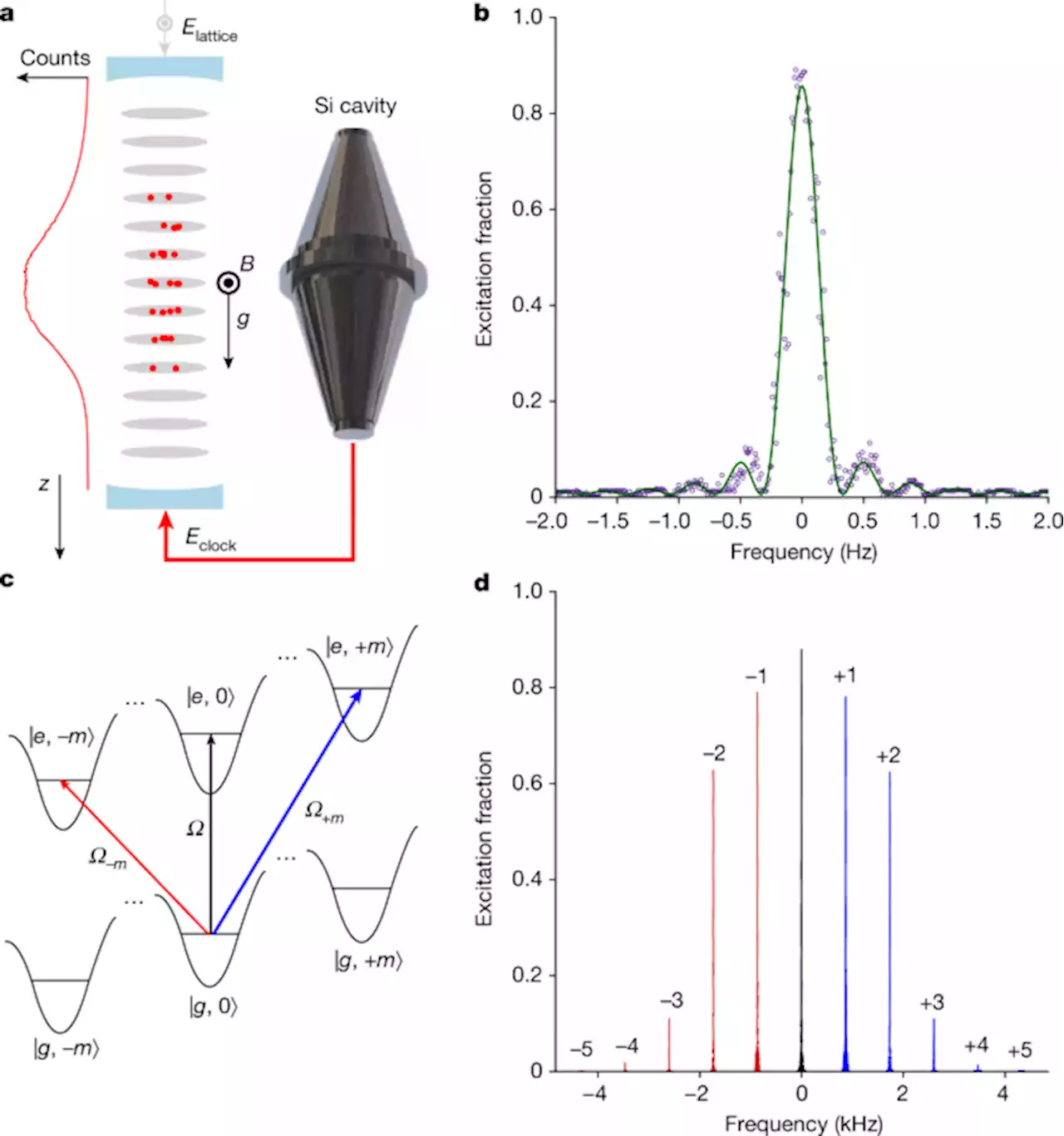 Resolving the gravitational redshift across a millimetre-scale atomic sample - NatureReducing the fractional uncertainty over the measurement of the frequency of an ensemble of trapped strontium atoms enables observation of the gravitational redshift at the submillimetre scale.
Resolving the gravitational redshift across a millimetre-scale atomic sample - NatureReducing the fractional uncertainty over the measurement of the frequency of an ensemble of trapped strontium atoms enables observation of the gravitational redshift at the submillimetre scale.
Read more »
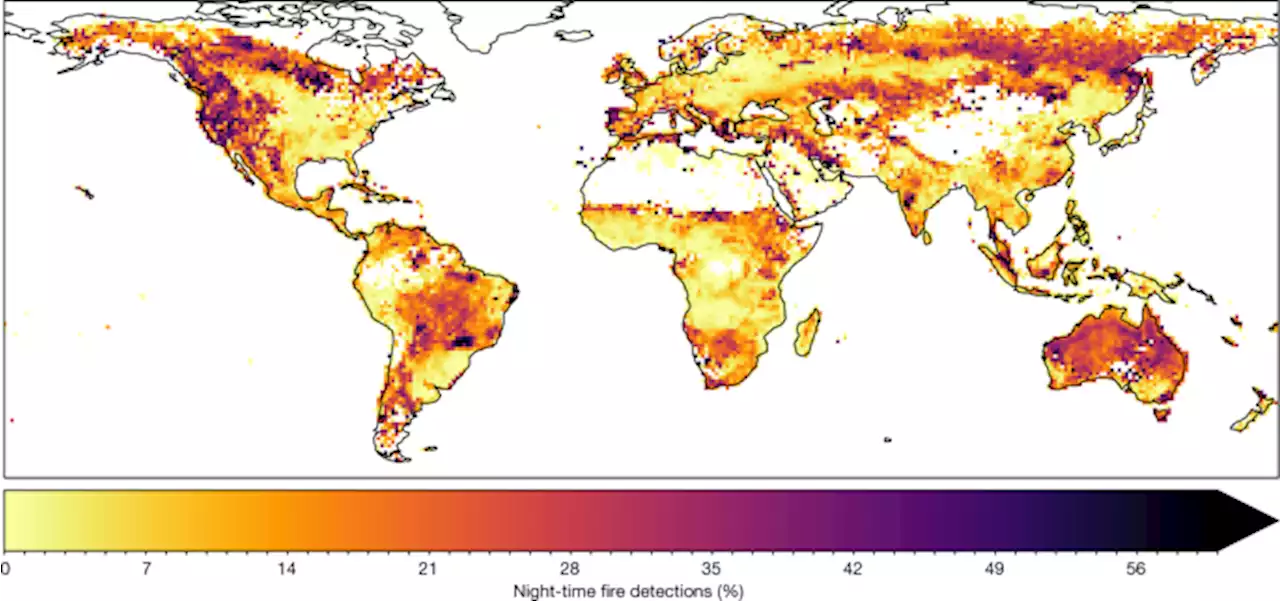 Warming weakens the night-time barrier to global fire - NatureAn analysis of satellite observations and climate data shows that night-time fire intensity has increased over the past two decades owing to hotter and drier nights under anthropogenic climate change.
Warming weakens the night-time barrier to global fire - NatureAn analysis of satellite observations and climate data shows that night-time fire intensity has increased over the past two decades owing to hotter and drier nights under anthropogenic climate change.
Read more »
