A team at Montana State University published research this week that shows how RNA, the close chemical cousin to DNA, can be edited using CRISPRs.
Apr 29 2024Montana State University The work reveals a new process in human cells that has potential for treating a wide variety of genetic diseases.
In our previous work, we used type-III CRISPRs to edit viral RNA in a test tube. But we wondered, can we program manipulation of RNA in a living human cell?" "We were confident that we could use these CRISPR systems to cut RNA in a programmable manner, but we were all surprised when we sequenced the RNA and realized that the cell had stitched the RNA back together in a way that removed the mutation," said Wiedenheft."The general belief is that there's not much point in repairing RNA," he said. "We speculated that RNA would be repaired in living human cells, and it turned out to be true.
RNA editing has important applications in the search for treatments of genetic diseases, Nemudryi said. RNA is a temporary copy of a cell's DNA, which serves as a template. Manipulating the template by editing DNA could cause unwanted and potentially irreversible collateral changes, but because RNA is a temporary copy, he said, edits made are essentially reversible and carry far less risk.
Research RNA Agriculture Bacteria Cas9 Cell Cell Biology CRISPR Cystic Fibrosis DNA Fibrosis Genetic Engineering Immune System Microbiology Mutation Palindromic Repeats Technology
Ireland Latest News, Ireland Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 State-by-state is the best approach for right to repair, says advocacy leaderGay Gordon-Byrne of the Repair Association says US at least is nearing a tipping point
State-by-state is the best approach for right to repair, says advocacy leaderGay Gordon-Byrne of the Repair Association says US at least is nearing a tipping point
Read more »
 Iowa State, Kansas State to open 2025 season in Dublin, IrelandThe game kicks off Aug. 23 and marks the first time Iowa State will play outside of the United States and just the second time for Kansas St
Iowa State, Kansas State to open 2025 season in Dublin, IrelandThe game kicks off Aug. 23 and marks the first time Iowa State will play outside of the United States and just the second time for Kansas St
Read more »
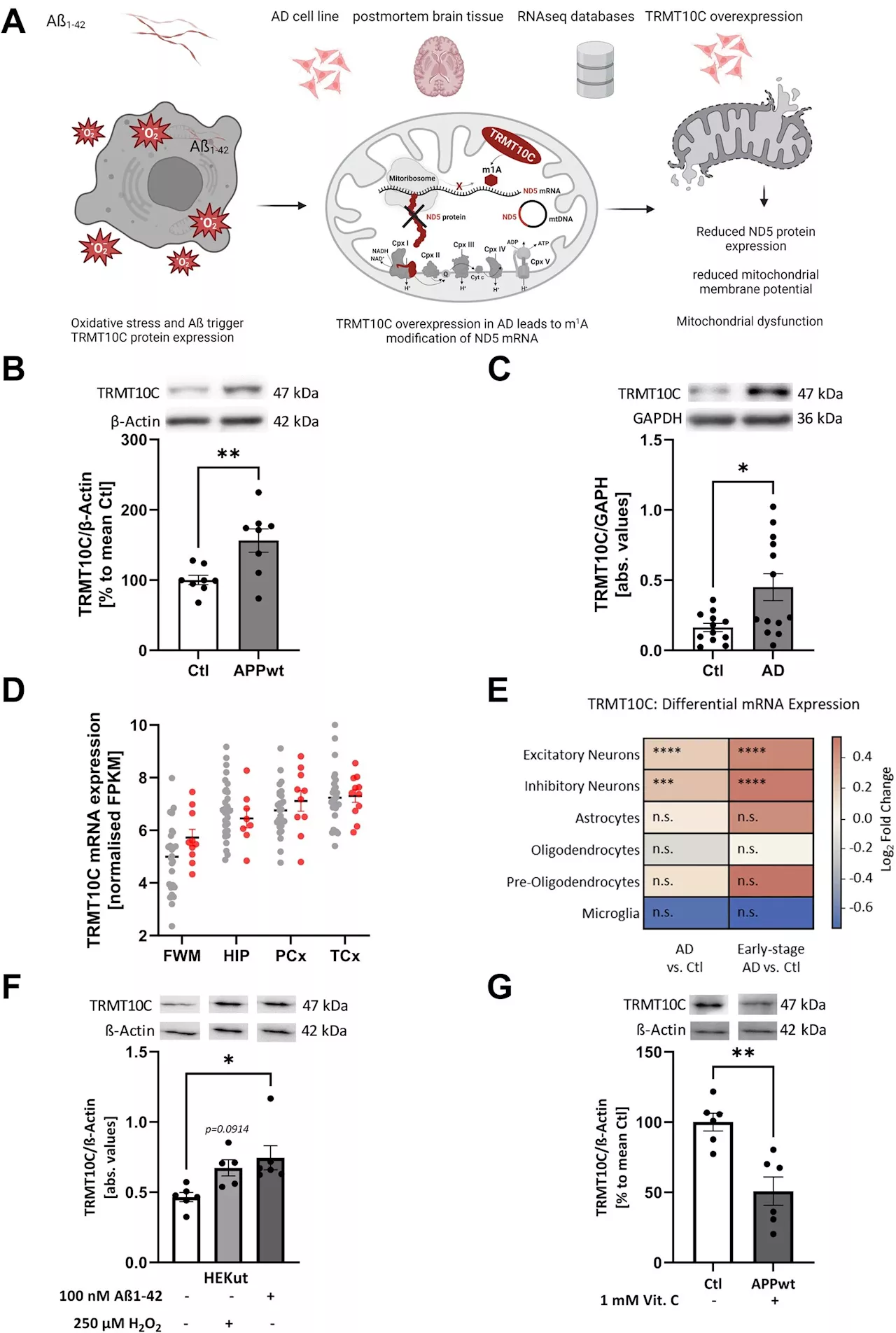 Study finds RNA modification is responsible for disruption of mitochondrial protein synthesis in Alzheimer's diseaseA team of researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) has identified a mechanism that causes mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's patients resulting in a reduction of the supply of energy to the brain.
Study finds RNA modification is responsible for disruption of mitochondrial protein synthesis in Alzheimer's diseaseA team of researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) has identified a mechanism that causes mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's patients resulting in a reduction of the supply of energy to the brain.
Read more »
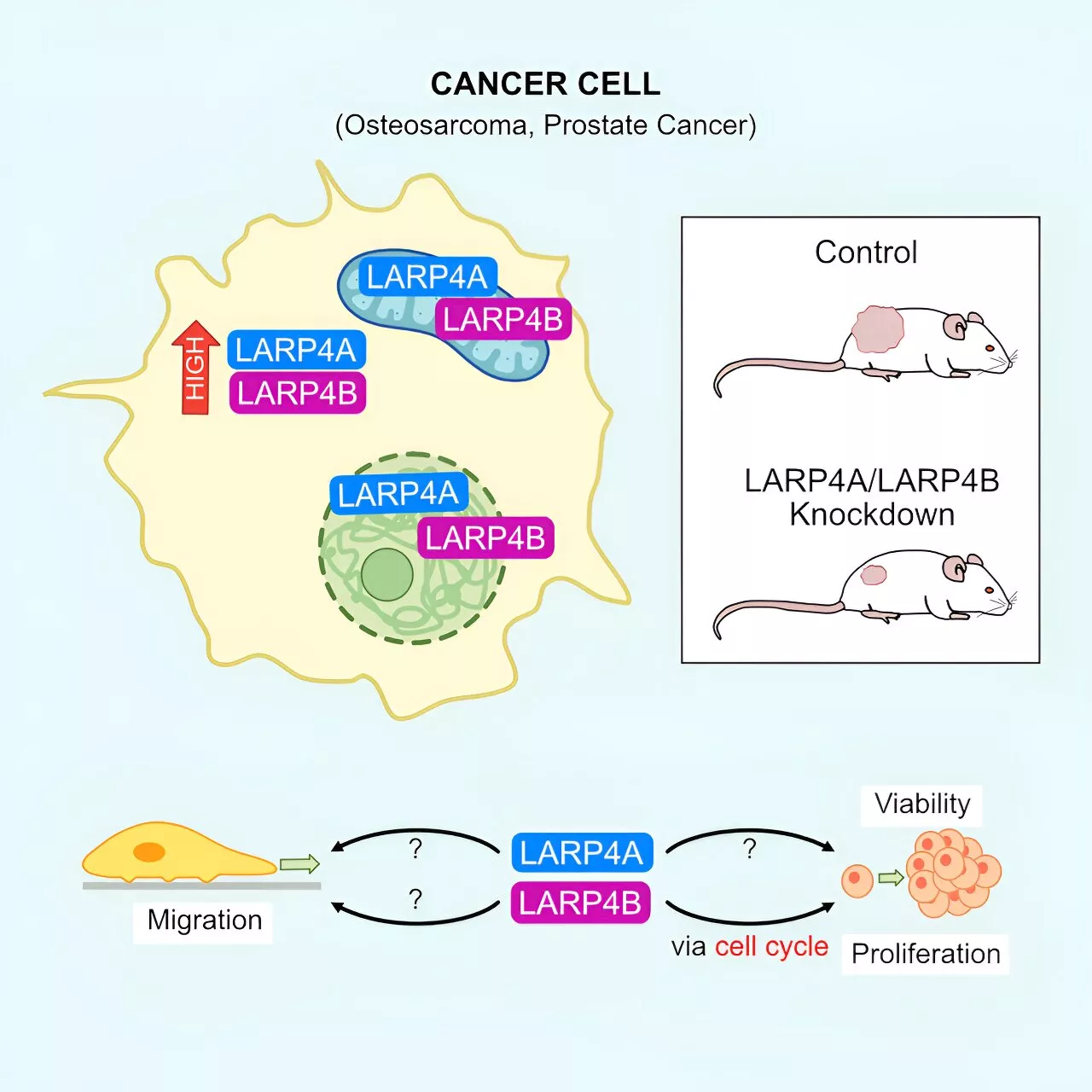 New potential avenues for cancer therapies through RNA-binding proteinsA new paper describes the role of two RNA-binding proteins in the development of sarcoma and carcinoma cancers, highlighting the important and emerging role of RNA-binding proteins in cancer research and offering a new avenue for therapeutic targets.
New potential avenues for cancer therapies through RNA-binding proteinsA new paper describes the role of two RNA-binding proteins in the development of sarcoma and carcinoma cancers, highlighting the important and emerging role of RNA-binding proteins in cancer research and offering a new avenue for therapeutic targets.
Read more »
 Cas13d-NCS: A game-changer in RNA virus defenseThe rise of RNA viruses like SARS-CoV-2 highlights the need for new ways to fight them. RNA-targeting tools like CRISPR/Cas13 are powerful but inefficient in the cytoplasm of cells, where many RNA viruses replicate.
Cas13d-NCS: A game-changer in RNA virus defenseThe rise of RNA viruses like SARS-CoV-2 highlights the need for new ways to fight them. RNA-targeting tools like CRISPR/Cas13 are powerful but inefficient in the cytoplasm of cells, where many RNA viruses replicate.
Read more »
 Unveiling the key role of RNA modification in HIV-1 survival and replicationA chemical modification in the HIV-1 RNA genome whose function has been a matter of scientific debate is now confirmed to be key to the virus's ability to survive and thrive after infecting host cells, a new study has found.
Unveiling the key role of RNA modification in HIV-1 survival and replicationA chemical modification in the HIV-1 RNA genome whose function has been a matter of scientific debate is now confirmed to be key to the virus's ability to survive and thrive after infecting host cells, a new study has found.
Read more »
