Microbial intervention strengthens the aged muscle and rejuvenates the skin through changes in the microbial structure and host gene expression, finds a study published in MicrobiomeJ. Read the paper here:
]; the threshold of logarithmic LDA score was 2.0. Spearman’s correlation coefficient was calculated for bacterial species that have more than 0.5% relative abundance in 12-month-old recipient mice using the psych R package.To examine the cognitive response of mice, a passive avoidance test was performed. A mouse was placed in a light chamber for 30 s and allowed to move to a dark chamber upon gate opening.
For the intraocular pressure test, mice were anesthetized using an intraperitoneal injection of xylazine and zolazepam and tiletamine . IOP was measured using a rebound tonometer , according to the manufacturer’s instructions. One trial result was obtained after six consecutive measurements, and the mean of consecutive trials was used for analyses.
Electroretinogram analysis was performed using Micron Ganzfeld ERG . The mouse was dark-adapted at least 12 h before the experiment for scotopic testing . After anesthesia, the pupil dilated as previously described. Once the pupil was fully dilated, we applied hypromellose 2.5% and inserted the electrodes. ERG was recorded using Micron Ganzfeld ERG, according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Scotopic ERG was obtained with increasing flash intensity at a range of −1.7 log cd/s/m.
For immunofluorescence, tissue sample preparation and blocking were performed in the same manner as described in immunohistochemistry. Then, the slides were probed at 4 °C overnight with the primary antibodies , labeled for 2 h with Cy3-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG or A488 donkey anti-mouse IgG , and stained with DAPI for 15 min.
QuantSeq 3′ mRNA-Seq reads were aligned using Bowtie2. Bowtie2 indices were either generated from the genome assembly sequence or representative transcript sequences for aligning to the genome and transcriptome. The alignment file was used for assembling transcripts, estimating their abundances, and detecting differential expression of genes. Raw read counts were normalized and differentially expressed genes were identified using the edgeR package .
Ireland Latest News, Ireland Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Association of indoor dust microbiota with cognitive function and behavior in preschool-aged children - MicrobiomeBackground Childhood cognitive development depends on neuroimmune interactions. Immunomodulation by early-life microbial exposure may influence neuropsychological function. In this study, we investigate the association between residential indoor microbiota and cognition and behavior among preschoolers. Results Indoor-settled dust bacterial and fungal characteristics were assessed using 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing (microbial diversity) and qPCR measurements (microbial loads). Child behavior was assessed using four scales: peer relationship, emotional, conduct, and hyperactivity was assessed by the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ). Cognitive function was assessed using four tasks of the Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB) software. The first two tasks were designed to assess attention and psychomotor speed (Motor Screening (MOT) and Big/Little Circle (BLC)) and the last two to evaluate the child’s visual recognition/working memory (Spatial Span (SSP) and Delayed Matching to Sample (DMS)). Among the 172 included children (age 4–6 years), we observed a 51% (95%CI;75%;9%) lower odds of children scoring not normal for hyperactivity and a decrease of 3.20% (95%CI, −6.01%; −0.30%) in BLC response time, for every IQR increase in fungal Shannon diversity. Contrarily, microbial loads were directly associated with SDQ scales and response time. For example, a 2-fold increase in Gram-positive bacterial load was associated with 70% (95%CI 18%; 156%) higher odds of scoring not normal for hyperactivity and an increase of 5.17% (95%CI 0.87%; 9.65%) in DMS response time. Conclusions Our findings show that early-life exposure to diverse indoor fungal communities is associated with better behavioral and cognitive outcomes, whereas higher indoor microbial load was associated with worse outcomes. Video Abstract
Association of indoor dust microbiota with cognitive function and behavior in preschool-aged children - MicrobiomeBackground Childhood cognitive development depends on neuroimmune interactions. Immunomodulation by early-life microbial exposure may influence neuropsychological function. In this study, we investigate the association between residential indoor microbiota and cognition and behavior among preschoolers. Results Indoor-settled dust bacterial and fungal characteristics were assessed using 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing (microbial diversity) and qPCR measurements (microbial loads). Child behavior was assessed using four scales: peer relationship, emotional, conduct, and hyperactivity was assessed by the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ). Cognitive function was assessed using four tasks of the Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB) software. The first two tasks were designed to assess attention and psychomotor speed (Motor Screening (MOT) and Big/Little Circle (BLC)) and the last two to evaluate the child’s visual recognition/working memory (Spatial Span (SSP) and Delayed Matching to Sample (DMS)). Among the 172 included children (age 4–6 years), we observed a 51% (95%CI;75%;9%) lower odds of children scoring not normal for hyperactivity and a decrease of 3.20% (95%CI, −6.01%; −0.30%) in BLC response time, for every IQR increase in fungal Shannon diversity. Contrarily, microbial loads were directly associated with SDQ scales and response time. For example, a 2-fold increase in Gram-positive bacterial load was associated with 70% (95%CI 18%; 156%) higher odds of scoring not normal for hyperactivity and an increase of 5.17% (95%CI 0.87%; 9.65%) in DMS response time. Conclusions Our findings show that early-life exposure to diverse indoor fungal communities is associated with better behavioral and cognitive outcomes, whereas higher indoor microbial load was associated with worse outcomes. Video Abstract
Read more »
 Five signs of poor gut health - from upset stomach to fatigueDr Sameer Sanghvi has highlighted the signs that could indicate a poor tummy.
Five signs of poor gut health - from upset stomach to fatigueDr Sameer Sanghvi has highlighted the signs that could indicate a poor tummy.
Read more »
 The gut microbiota in multiple sclerosis varies with disease activity - Genome MedicineBackground Multiple sclerosis is a chronic immune-mediated disease of the brain and spinal cord resulting in physical and cognitive impairment in young adults. It is hypothesized that a disrupted bacterial and viral gut microbiota is a part of the pathogenesis mediating disease impact through an altered gut microbiota-brain axis. The aim of this study is to explore the characteristics of gut microbiota in multiple sclerosis and to associate it with disease variables, as the etiology of the disease remains only partially known. Methods Here, in a case-control setting involving 148 Danish cases with multiple sclerosis and 148 matched healthy control subjects, we performed shotgun sequencing of fecal microbial DNA and associated bacterial and viral microbiota findings with plasma cytokines, blood cell gene expression profiles, and disease activity. Results We found 61 bacterial species that were differentially abundant when comparing all multiple sclerosis cases with healthy controls, among which 31 species were enriched in cases. A cluster of inflammation markers composed of blood leukocytes, CRP, and blood cell gene expression of IL17A and IL6 was positively associated with a cluster of multiple sclerosis-related species. Bacterial species that were more abundant in cases with disease-active treatment-naïve multiple sclerosis were positively linked to a group of plasma cytokines including IL-22, IL-17A, IFN-β, IL-33, and TNF-α. The bacterial species richness of treatment-naïve multiple sclerosis cases was associated with number of relapses over a follow-up period of 2 years. However, in non-disease-active cases, we identified two bacterial species, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Gordonibacter urolithinfaciens, whose absolute abundance was enriched. These bacteria are known to produce anti-inflammatory metabolites including butyrate and urolithin. In addition, cases with multiple sclerosis had a higher viral species diversity and a higher abundance of Caudovirales b
The gut microbiota in multiple sclerosis varies with disease activity - Genome MedicineBackground Multiple sclerosis is a chronic immune-mediated disease of the brain and spinal cord resulting in physical and cognitive impairment in young adults. It is hypothesized that a disrupted bacterial and viral gut microbiota is a part of the pathogenesis mediating disease impact through an altered gut microbiota-brain axis. The aim of this study is to explore the characteristics of gut microbiota in multiple sclerosis and to associate it with disease variables, as the etiology of the disease remains only partially known. Methods Here, in a case-control setting involving 148 Danish cases with multiple sclerosis and 148 matched healthy control subjects, we performed shotgun sequencing of fecal microbial DNA and associated bacterial and viral microbiota findings with plasma cytokines, blood cell gene expression profiles, and disease activity. Results We found 61 bacterial species that were differentially abundant when comparing all multiple sclerosis cases with healthy controls, among which 31 species were enriched in cases. A cluster of inflammation markers composed of blood leukocytes, CRP, and blood cell gene expression of IL17A and IL6 was positively associated with a cluster of multiple sclerosis-related species. Bacterial species that were more abundant in cases with disease-active treatment-naïve multiple sclerosis were positively linked to a group of plasma cytokines including IL-22, IL-17A, IFN-β, IL-33, and TNF-α. The bacterial species richness of treatment-naïve multiple sclerosis cases was associated with number of relapses over a follow-up period of 2 years. However, in non-disease-active cases, we identified two bacterial species, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Gordonibacter urolithinfaciens, whose absolute abundance was enriched. These bacteria are known to produce anti-inflammatory metabolites including butyrate and urolithin. In addition, cases with multiple sclerosis had a higher viral species diversity and a higher abundance of Caudovirales b
Read more »
 How gut bacteria evade the immune systemResearchers from the Max Planck Institute for Biology Tübingen address the long-standing question of how benign gut microbes evade the immune system. In doing so, they also reshape our understanding of how immune receptors interact with the bacterial motility protein flagellin.
How gut bacteria evade the immune systemResearchers from the Max Planck Institute for Biology Tübingen address the long-standing question of how benign gut microbes evade the immune system. In doing so, they also reshape our understanding of how immune receptors interact with the bacterial motility protein flagellin.
Read more »
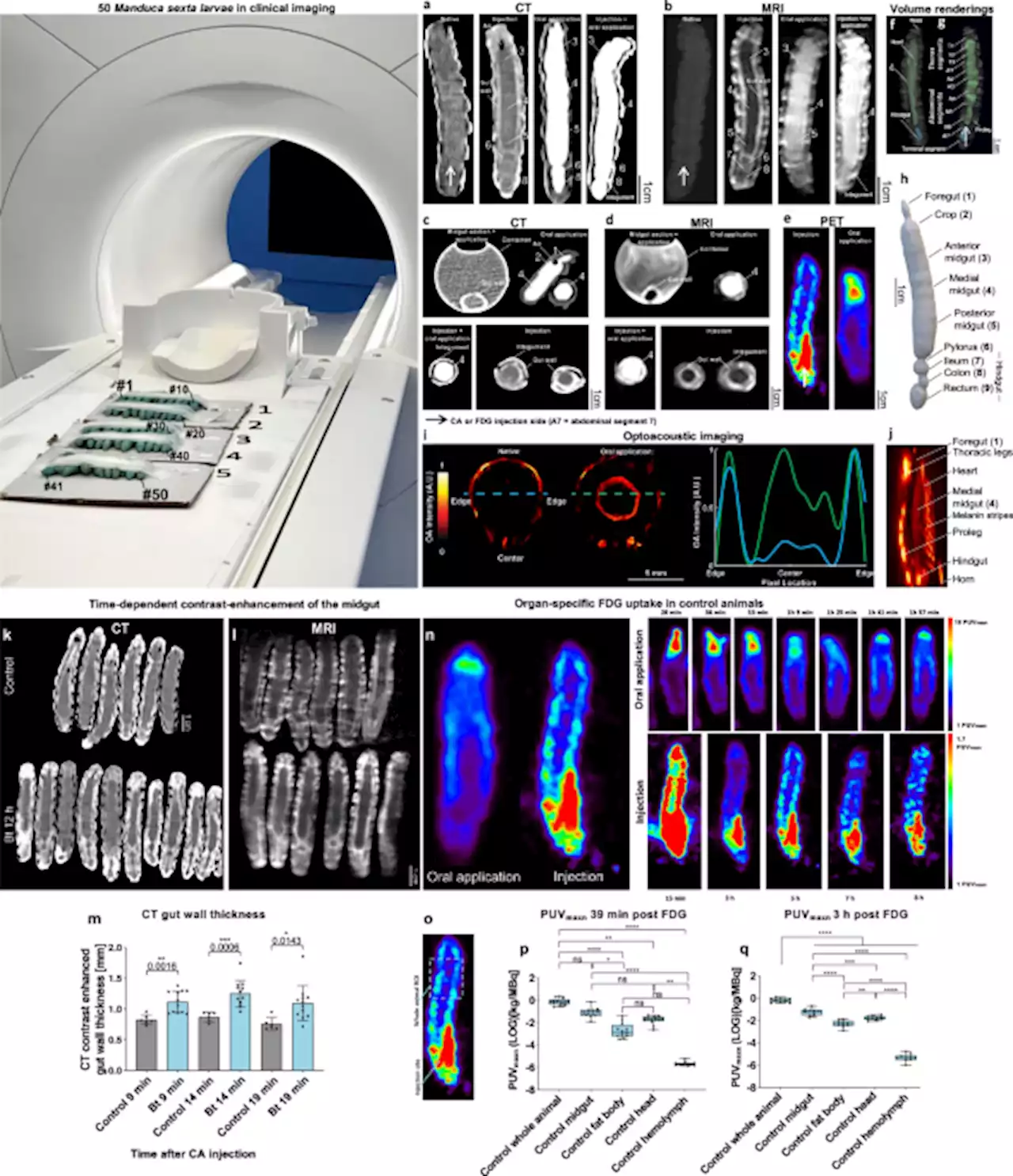 High-throughput screening of caterpillars as a platform to study host–microbe interactions and enteric immunity - Nature CommunicationsHere, combining diagnostic imaging modalities and in vivo assays, Windfelder and colleagues established tobacco hornworm larvae Manduca sexta as an alternative high-throughput platform to study the innate immunity of the gut and host-pathogen interactions. Using the platform, the authors identify mediators of gut inflammation, differentiate pathogens from gut mutualist bacteria, and demonstrate pharmacological interventions.
High-throughput screening of caterpillars as a platform to study host–microbe interactions and enteric immunity - Nature CommunicationsHere, combining diagnostic imaging modalities and in vivo assays, Windfelder and colleagues established tobacco hornworm larvae Manduca sexta as an alternative high-throughput platform to study the innate immunity of the gut and host-pathogen interactions. Using the platform, the authors identify mediators of gut inflammation, differentiate pathogens from gut mutualist bacteria, and demonstrate pharmacological interventions.
Read more »
